Answer:
w = 1.53 rad / s
Step-by-step explanation:
For this exercise we will use conservation of angular momentum. Let's start by defining our system as formed for the bar and the ball, for which all the torques formed are internal and consequently the angular momentum is conserved.
Initial moment. Just before crash
L₀ = m v₁ L₁
final moment. Right after the crash
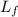 = I_bar w + m v₂ L₁
= I_bar w + m v₂ L₁
where L₁ is the distance of the ball L₁ = 1,6m and m its mass 4 kg, let's take as the direction of the positive initial velocity
The moment of inertia of a bar that rotates at its end is
I_bar = ⅓ M L²
L₀ = L_{f}
m v₁ L₁ = (⅓ M L²) w + m v₂ L₁
w = m L₁ (v₁ - v₂) 3 / ML²
let's calculate
velocity v₁ = 1.6 m /s and its bounce v₂ = - 5 m / s
M = W / g
M = 90 / 9.8
M = 9.19 kg
w = 4 1.6 (1.6 + 5) 3 / (9.19 3 2)
w = 1.53 rad / s