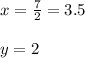Answer:
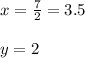
Explanation:
The addition method (elimination method) allows us to combine two equations in such a way that the resulting equation has only one variable. Then we can use simple algebraic methods to solve that variable
Let:
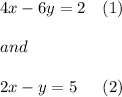
Let's multiply (2) by -2:
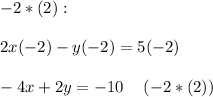
Now, add (1) and (-2*(2)):
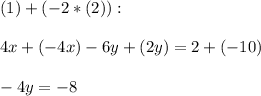
Hence, solving for y:
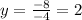
Replacing y into (2):
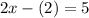
Solving for x:
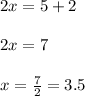
Therefore: