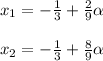Answer:
Explanation:
Given:-
- The following system of equations is given:
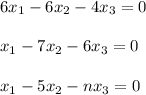
Solution:-
- The matrix equation consists of coefficient matrix "A" and a variable matrix " x ". These two matrices undergo multiplication to yield a solution column vector "b".
- The matrix A, is a symmetrical square matrix with its elements representing the coefficients of each variable as follows:
![A = \left[\begin{array}{ccc}a_1_1&a_1_2&a_1_3\\a_2_1&a_2_2&a_2_3\\a_3_1&a_3_2&a_3_3\end{array}\right]](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/mathematics/college/c84x9e0cfha45wn98uaibcmh27q3mctqxk.png)
- Where the elements first subscript denotes the equation number and second subscript denotes the variable number.
![A = \left[\begin{array}{ccc}6&-6&-4\\1&-7&-6\\1&5&n\end{array}\right]](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/mathematics/college/hl40p3sps2dyw1qmoxhyehnk55ft3fdko1.png)
- Similarly, the variable matrix " X " is a column vector that lists all the variables in the the system of equations in a ascending order.
![X = \left[\begin{array}{c}x_1&x_2&x_3\end{array}\right]](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/mathematics/college/y14fjvrresavy1e9io28b4nuf5juxag3lf.png)
- The solution vector " b " is the corresponding solution or any number written on the right hand side of the equals to sign " = " :
![b = \left[\begin{array}{c}0&2&-2\end{array}\right]](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/mathematics/college/vvjt5yz7gq46fa3q3gme8m28mzdeh54p05.png)
- Now, we can express the given system in the asked format:
![A*X = b\\\\\left[\begin{array}{ccc}6&-6&-4\\1&-7&-6\\1&5&n\end{array}\right]*\left[\begin{array}{c}x_1&x_2&x_3\end{array}\right] = \left[\begin{array}{c}0&2&-2\end{array}\right]](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/mathematics/college/lm9apv6awpof4qsb7c5sgzypx6expb32ka.png)
- The augmented matrix is a matrix that combines the coefficient matrix " A " and the solution vector " b ". A solution vector "b" as an extra column to the coefficient matrix:
![[ A | b ]\\\\ \left[\begin{array}{ccccc}6&-6&-4&|&0\\1&-7&-6&|&2\\1&5&n&|&-2\end{array}\right]](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/mathematics/college/ucvaaxo1wdrk2zjp2qo47gfcnq43oq016m.png)
- Now we will perform row reduction operation such that the system is consistent and has infinite number of solution.
- Row operation: R3 - R2 & R1/6
![\left[\begin{array}{ccccc}1&-1&-(2)/(3) &|&0\\1&-7&-6&|&2\\0&12&n+6&|&-4\end{array}\right]](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/mathematics/college/kuvq9vselfcxch3od19e6ela349il1kopn.png)
- Row operation: R2 - R1 & R3 / 12
![\left[\begin{array}{ccccc}1&-1&-(2)/(3) &|&0\\0&-6&-(16)/(3) &|&2\\0&1&(n+6)/(12) &|&-(1)/(3)\end{array}\right]](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/mathematics/college/5hvrw5awvt8pou343hxahnrvgvgl4wtpeo.png)
- Row operation: R2 / 6
![\left[\begin{array}{ccccc}1&-1&-(2)/(3) &|&0\\0&-1&-(8)/(9) &|&(1)/(3) \\0&1&(n+6)/(12) &|&-(1)/(3)\end{array}\right]](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/mathematics/college/eonquvdhsfpe1iv04khik9oip6zrdu3i89.png)
For the above system to be consistent and have infinite many solution then the coefficient of " x3 " for the 2nd and 3rd row must be equal:
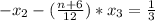
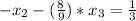
The coefficient of " x_3 " must be equal:
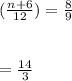
- The augmented matrix in reduced form becomes:
![\left[\begin{array}{ccccc}1&-1&-(2)/(3) &|&0\\0&1&(8)/(9) &|&-(1)/(3) \\0&0&0 &|&0\end{array}\right]](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/mathematics/college/l52m600seqkdqmi7fi8j8ggnrrkjhyroym.png)
Answer: Rank = Number of non-zero rows = 2
- The number of linearly independent rows are equal to the rank of the augmented matrix.
Hence,
Answer: Number of linearly independent rows = 2
Row operation: R1 + R2
![\left[\begin{array}{ccccc}1&0&(2)/(9) &|&-(1)/(3) \\0&1&(8)/(9) &|&-(1)/(3) \\0&0&0 &|&0\end{array}\right]](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/mathematics/college/s9yhuklgee58qyugasf8071kn99twc7vdb.png)
- The variable "x_3" will take any arbitrary value for which the solution holds infinitely many solutions.
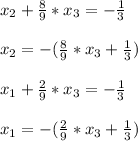
- Taking x_3 = α:
Answers: