Answer:
We conclude that the true average percentage of Silicon Dioxide is smaller than 5.5.
Explanation:
We are given that the desired percentage of Silicon Dioxide (SiO2) in a certain type of aluminous cement is 5.5.
16 independently obtained samples are analyzed and a sample mean of 5.25 was obtained. Suppose that the percentage of SiO2 in a sample is normally distributed with a sigma of 0.3.
Let
 = true average percentage of Silicon Dioxide.
= true average percentage of Silicon Dioxide.
So, Null Hypothesis,
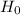 :
:

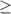 5.5 {means that the true average is greater than or equal to 5.5}
5.5 {means that the true average is greater than or equal to 5.5}
Alternate Hypothesis,
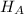 :
:
 < 5.5 {means that the true average is smaller than 5.5}
< 5.5 {means that the true average is smaller than 5.5}
The test statistics that would be used here One-sample z test statistics as we know about the population standard deviation;
T.S. =
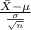 ~ N(0,1)
~ N(0,1)
where,
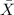 = sample mean percentage of Silicon Dioxide = 5.25
= sample mean percentage of Silicon Dioxide = 5.25
σ = population standard deviation = 0.3
n = sample size = 16
So, the test statistics =
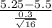
= -3.33
The value of z test statistics is -3.33.
Now, the P-value of the test statistics is given by;
P-value = P(Z < -3.33) = 1 - P(Z
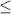 3.33)
3.33)
= 1 - 0.9996 = 0.0004
Since, the P-value of the test statistics is less than the level of significance as 0.0004 < 0.01, so we have sufficient evidence to reject our null hypothesis as it will fall in the rejection region due to which we reject our null hypothesis.
Therefore, we conclude that the true average percentage of Silicon Dioxide is smaller than 5.5.