Answer:
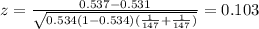
Now we can calculate the p value with the following probability taking in count the alternative hypothesis:
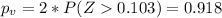
For this case since the p value is large enough we have enough evidence to FAIL to reject the null hypothesis and we can't conclude that we have significant differences between the two proportions analyzed.
Explanation:
Information provided
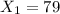 represent the number of New Yorkers familiar with the brand
represent the number of New Yorkers familiar with the brand
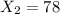 represent the number of Californians familiar with the brand
represent the number of Californians familiar with the brand
 sample of New Yorkers
sample of New Yorkers
 sample of Californians
sample of Californians
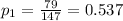 represent the proportion New Yorkers familiar with the brand
represent the proportion New Yorkers familiar with the brand
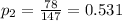 represent the proportion of Californians familiar with the brand
represent the proportion of Californians familiar with the brand
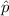 represent the pooled estimate of p
represent the pooled estimate of p
z would represent the statistic
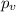 represent the value
represent the value
System of hypothesis
We want to verify if the two proportions of interest for this case are equal, the system of hypothesis would be:
Null hypothesis:
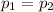
Alternative hypothesis:
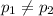
The statistic would be given by:
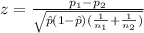 (1)
(1)
Where
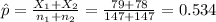
Repalcing the info given we got:
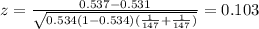
Now we can calculate the p value with the following probability taking in count the alternative hypothesis:
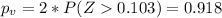
For this case since the p value is large enough we have enough evidence to FAIL to reject the null hypothesis and we can't conclude that we have significant differences between the two proportions analyzed.