Answer:
Concentration of water at equilibrium is 0.1177 M.
Step-by-step explanation:
Balanced equation:
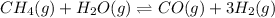
Equilibrium concentration of
 , [
, [
 ] =
] =
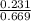 M = 0.345 M
M = 0.345 M
Equilibrium concentration of CO, [CO] =
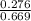 M = 0.413 M
M = 0.413 M
Equilibrium concentration of
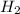 , [
, [
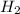 ] =
] =
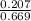 M = 0.309 M
M = 0.309 M
Equilibrium constant for the given reaction in terms of concentration,
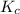 is expressed as:
is expressed as:
![K_(c)=([CO][H_(2)]^(3))/([CH_(4)][H_(2)O])](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/7fvvy4g0gumpuee0qgj07x7p76ilgc1phg.png)
![\Rightarrow [H_(2)O]=([CO][H_(2)]^(3))/([CH_(4)].K_(c))=((0.413)* (0.309)^(3))/((0.345)* (0.30))= 0.1177](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/9dg7tmzn4t15nyilbtojn1co8kkkd8b4h5.png)
Hence, concentration of water at equilibrium is 0.1177 M