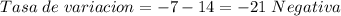Answer:
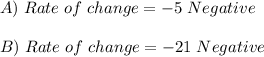
Explanation:
Given a function
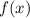 , we called the rate of change to the number that represents the increase or decrease that the function experiences when increasing the independent variable from one value "
, we called the rate of change to the number that represents the increase or decrease that the function experiences when increasing the independent variable from one value "
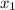 " to another "
" to another "
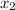 ".
".
The rate of change of
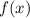 between
between
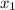 and
and
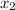 can be calculated as follows:
can be calculated as follows:
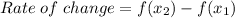
For:
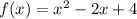
Let's find
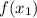 and
and
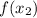 , where:
, where:
![[x_1,x_2]=[-4,3]](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/mathematics/high-school/6nbh0tldxevzcvrk43zuow4v357nfw6sze.png)
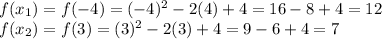
So:
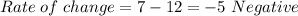
And for:
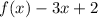
Let's find
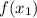 and
and
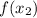 , where:
, where:
![[x_1,x_2]=[-4,3]](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/mathematics/high-school/6nbh0tldxevzcvrk43zuow4v357nfw6sze.png)
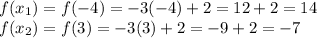
So:
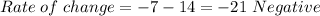
Translation:
Dada una función
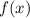 , llamábamos tasa de variación al número que representa el aumento o disminución que experimenta la función al aumentar la variable independiente de un valor "
, llamábamos tasa de variación al número que representa el aumento o disminución que experimenta la función al aumentar la variable independiente de un valor "
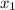 " a otro "
" a otro "
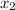 ".
".
La tasa de variación de
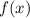 entre
entre
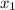 y
y
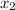 , puede ser calculada de la siguiente forma:
, puede ser calculada de la siguiente forma:
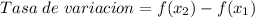
Para:
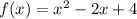
Encontremos
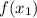 y
y
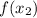 , donde:
, donde:
![[x_1,x_2]=[-4,3]](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/mathematics/high-school/6nbh0tldxevzcvrk43zuow4v357nfw6sze.png)
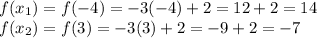
Entonces:
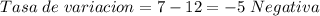
Y para:
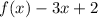
Encontremos
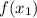 y
y
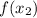 , donde:
, donde:
![[x_1,x_2]=[-4,3]](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/mathematics/high-school/6nbh0tldxevzcvrk43zuow4v357nfw6sze.png)
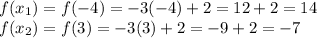
Entonces: