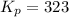Answer:
The pressure equilibrium constant is
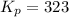
Step-by-step explanation:
From the question we are told that
The volume of the flask is
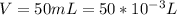
The pressure of sulfur dioxide is
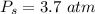
The pressure of oxygen gas
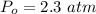
The pressure of sulfur trioxide at equilibrium is
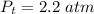
The chemical equation for this reaction is
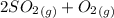 ⇄
⇄
The partial pressure of oxygen at equilibrium is mathematically evaluated as
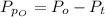
Substituting values
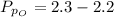
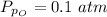
The partial pressure of sulfur dioxide at equilibrium is mathematically evaluated as
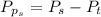
Substituting values
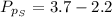
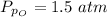
From the chemical equation pressure constant is mathematically represented as
![K_p = ([P_t]^2)/([P_p__(o)) ]^2 [P_p__(s)}]}](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/lep9my00ocip0olqun6zrczgml0bbzuzah.png)
Substituting values
![K_p = \frac{[2.2]^2}{[ 0.1 ]^2 [{ 1.5}]}](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/6iolycq7evdn1zr2udf61jgnsx80fx7wrh.png)