Answer: See the image attachment below.
=============================================================
Step-by-step explanation:
If the money is compounded semiannually at a rate of 8%, then this means the multiplier (common ratio) is b = 1+r/n = 1+0.08/2 = 1.04
- r = 0.08 = 8% annual interest rate
- n = 2 = compounding twice a year, aka semiannually, aka every 6 months.
In short, b = 1.04 is our growth multiplier. It says that the money is growing by 4% each 6 month period. Each time x goes up by 1, y increases by 4%. The starting amount is a = 2100 dollars.
We go from the template of
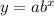 to
to
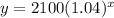
Use that equation to fill out the table. For instance, if x = 2 then,
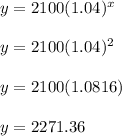
Meaning that after 2 semiannual periods (aka 2*6 = 12 months = 1 year), we'd have $2,271.36 in the account.
Repeat this for the other x values mentioned to get the table shown below. To fill out the final column of the first row, you'll look at the very bottom of the table in the previous column. Four semiannual periods is equal to 2 years.
--------------
These steps are repeated for the second row of the table.
This time the growth multiplier is b = 1 + r/n = 1 + 0.14/12 = 1.0116667 approximately. The starting amount is a = 700
So that's how we go from
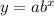 to
to
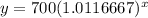
Like before, you'd plug in the various x values to find their paired y counterparts.
Example:
Plug in x = 18

The values are approximate. After 18 months, aka 18/12 = 1.5 years = 1 yr + 6 months, we'd have about $862.53 in the account.