Answer:
a) [Ag+]dilute = 6.363 × 10⁻¹⁶ M
b) 1.273 × 10⁻¹⁶
c) 2.629×10⁻¹⁹ M Thus; the value for [Ag+ ]dilute will be too low
Step-by-step explanation:
In an Ag | Ag+ concentration cell ,
The anode reaction can be written as :
Ag ----> Ag+(dilute) + e- &:
The cathode reaction can be written as:
Ag+(concentrated) + e- ----> Ag
The Overall Reaction : is
Ag+(concentrated) -----> Ag+(dilute)
However, the Standard Reduction potential of cell = E°cell = 0
( since both cathode and anode have same Ag+║Ag )
Also , given that the theoretical slope is - 0.0591 V
Therefore; the reduction potential of cell ; i.e
Ecell = E°cell - 0.0591 V × log ( [Ag+]dilute / [Ag+]concentrated )
0.839 V = 0 - 0.0591 V × log ( [Ag+]dilute / ( 1.0 × 10⁻¹ M ) )
log ( [Ag+]dilute / ( 1.0 × 10⁻¹ M ) ) = - 14.1963
[Ag+]dilute =
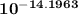 × 1.0 × 10⁻¹ M
× 1.0 × 10⁻¹ M
[Ag+]dilute = 6.363 × 10⁻¹⁶ M
b)
AgI ----> Ag + (dilute) + I⁻
So , Solubility product = Ksp = [Ag⁺]dilute × [I⁻]
= 6.363 × 10⁻¹⁶ M × 0.20 M
= 1.273 × 10⁻¹⁶
c) If s/he mistakenly uses 1.039 V as Ecell; then the value for [Ag+]dilute will be :
Ecell = E°cell - 0.0591 V × log ( [Ag+]dilute / [Ag+]concentrated )
1.039 V = 0 - 0.0591 V × log ( [Ag+]dilute / ( 1.0 × 10⁻¹ M ) )
log ( [Ag+]dilute / ( 1.0 × 10⁻¹ M ) ) = - 17.5804
[Ag+]dilute =
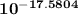 × 1.0 × 10⁻¹ M
× 1.0 × 10⁻¹ M
[Ag+]dilute = 2.629×10⁻¹⁹ M
Thus, the value for [Ag+ ]dilute will be too low