Answer:
We conclude that in the population of all senior executives, different from 40% say that the most common job interview mistake is to have little or no knowledge of the company.
Explanation:
We are given that in a survey of 155 senior executives, 48.4% said that the most common job interview mistake is to have little or no knowledge of the company.
We have to use a 0.05 significance level to test the claim that in the population of all senior executives, 40% say that the most common job interview mistake is to have little or no knowledge of the company.
Let p = population proportion of senior executives who said that the most common job interview mistake is to have little or no knowledge of the company
So, Null Hypothesis,
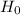 : p = 40% {means that in the population of all senior executives, 40% say that the most common job interview mistake is to have little or no knowledge of the company}
: p = 40% {means that in the population of all senior executives, 40% say that the most common job interview mistake is to have little or no knowledge of the company}
Alternate Hypothesis,
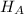 : p
: p
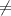 40% {means that in the population of all senior executives, different from 40% say that the most common job interview mistake is to have little or no knowledge of the company}
40% {means that in the population of all senior executives, different from 40% say that the most common job interview mistake is to have little or no knowledge of the company}
The test statistics that would be used here One-sample z test for proportions;
T.S. =
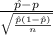 ~ N(0,1)
~ N(0,1)
where,
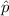 = sample proportion of senior executives who said that the most common job interview mistake is to have little or no knowledge of the company = 48.4%
= sample proportion of senior executives who said that the most common job interview mistake is to have little or no knowledge of the company = 48.4%
n = sample of senior executives = 155
So, the test statistics =
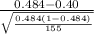
= 2.09
The value of z test statistics is 2.09.
Also, P-value of the test statistics is given by;
P-value = P(Z > 2.09) = 1 - P(Z
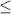 2.09)
2.09)
= 1 - 0.9817 = 0.0183
Now, at 0.05 significance level the z table gives critical values of -1.96 and 1.96 for two-tailed test.
Since our test statistic does not lie within the range of critical values of z, so we have sufficient evidence to reject our null hypothesis as it will fall in the rejection region due to which we reject our null hypothesis.
Therefore, we conclude that in the population of all senior executives, different from 40% say that the most common job interview mistake is to have little or no knowledge of the company.