Answer:
Moles:
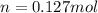
Molar mass:
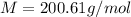
Step-by-step explanation:
Hello,
In this case, we can use the ideal gas equation to compute the moles of the gas sample as shown below:
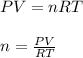
Thus, we should use the pressure in atm as follows:
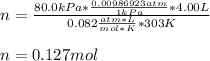
Moreover, the molar mass is obtained by dividing the given mass by the obtained moles:
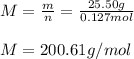
Best regards.