Answer:
B. Simplify both sides of the equation to get
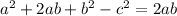 ; then subtract 2ab and add
; then subtract 2ab and add
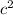 to both sides of the equation
to both sides of the equation
Explanation:
Given
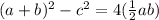
Required
Describe the next steps to
First, we open all brackets
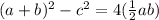
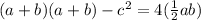
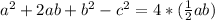
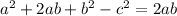
At this point, options A and C are incorrect because they didn't present the right result of the expression.
So, we have options B and D to consider
The next step is to subtract 2ab from both sides
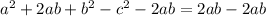
Collect like terms
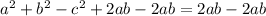
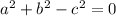
Lastly, to prove the Pythagoras theorem, the equation has to be in form of
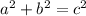 ; meaning the
; meaning the
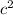 is added to both sides; See below
is added to both sides; See below
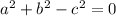
Add
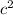 to both sides
to both sides
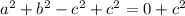
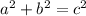
At this point, only option B completes Kira's proof