Answer:
459.126 grams of calcium chloride is needed to prepare 2.657 L of a 1.56 M solution
Step-by-step explanation:
Molarity is a measure of the concentration of a solute in a solution that indicates the amount of moles of solute that appear dissolved in one liter of the mixture. In other words, molarity is the number of moles of solute that are dissolved in a given volume.
The Molarity of a solution is determined by the following expression:
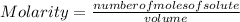
Molarity is expressed in units
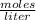
In this case:
- Molarity: 1.56 M= 1.56
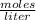
- Number of moles of calcium chlorine= ?
- Volume= 2.657 liters
Replacing:
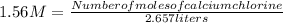
Solving:
Number of moles of calcium chlorine= 1.56 M* 2.657 liters
Number of moles of calcium chlorine= 4.14 moles
In other side, you know:
- Ca: 40 g/mole
- Cl: 35.45 g/mole
Then the molar mass of the calcium chloride CaCl₂ is:
CaCl₂= 40 g/mole + 2* 35.45 g/mole= 110.9 g/mole
Now it is possible to apply the following rule of three: if in 1 mole there is 110.9 g of CaCl₂, in 4.14 moles of the compound how much mass is there?
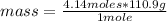
mass= 459.126 g
459.126 grams of calcium chloride is needed to prepare 2.657 L of a 1.56 M solution