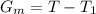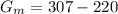Answer:
The extent of greenhouse effect on mars is

Step-by-step explanation:
From the question we are told that
The albedo value of Mars is
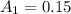
The albedo value of Mars is
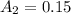
The surface temperature of Mars is
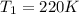
The surface temperature of Venus is
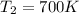
The distance of Mars from the sun is
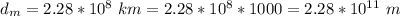
The distance of Venus from sun is
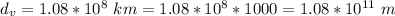
The radius of the sun is

The energy flux is
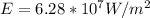
The solar constant for Mars is mathematically represented as
![T = [(E R^2 (1- A_1))/(\sigma d_m) ]](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/physics/college/wcuxh61y7xxuvm8whyh75bm8trqvbtorhn.png)
Where
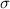 is the Stefan's constant with a value
is the Stefan's constant with a value
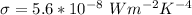
So substituting values
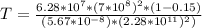
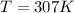
So the greenhouse effect on Mars is