Answer:
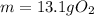
Step-by-step explanation:
Hello,
In this case, by using the ideal gas equation, we first compute the moles of oxygen at the given volume, pressure and temperature:
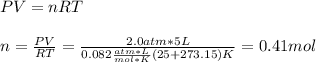
Then, since molar mass of gaseous oxygen is 32 g/mol, we compute the contained mass in grams as shown below:
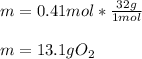
Best regards.