Answer:
The new volume is 2415 mL
Step-by-step explanation:
The STP conditions refer to the standard temperature and pressure. Pressure values at 1 atmosphere and temperature at 0 ° C are used and are reference values for gases.
Boyle's law says that the volume occupied by a given gas mass at constant temperature is inversely proportional to the pressure and is expressed mathematically as:
P * V = k
Charles's law is a law that says that when the amount of gas and pressure are kept constant, the ratio between volume and temperature will always have the same value:
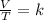
Gay-Lussac's law indicates that when there is a constant volume, as the temperature increases, the gas pressure increases. And when the temperature is decreased, the gas pressure decreases. This can be expressed mathematically in the following way:
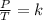
Combined law equation is the combination of three gas laws called Boyle's, Charlie's and Gay-Lusac's law:
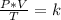
Having two different states, an initial state and an final state, it is true:
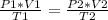
In this case:
- P1= 0.9 atm
- V1=4,600 mL= 4.6 L (being 1 L=1,000 mL)
- T1= 195 °C= 468 °K (being 0°C=273°K)
The final state 2 is in STP conditions:
- P2= 1 atm
- V2= ?
- T2= 0°C= 273 °K
Replacing:
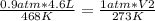
Solving:
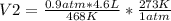
V2= 2.415 L =2,415 mL
The new volume is 2415 mL