Answer:
a) 15.37 mm
b)
c) 5.7186 W/m². K
d) 0.60 m
Step-by-step explanation:
Given that :
The surface temperature = 130°C = ( 130+ 273 ) K = 473 K
suspended in quiescent air at 25°C = ( 25 + 273 ) K = 298 K
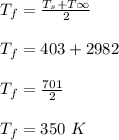
Atmospheric Pressure = 1 atm
The properties obtained from Table A - 4 include :
v =
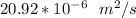
k = 0.03 W/m K
Pr = 0.700
η = 5
![Gr_x = 9.8[T_s - T \infty] (x^3)/(v^2)](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/engineering/college/h8w8xrnio2odc06acu3p0q8nq0pcfk7g5x.png)
![Gr_x = 9.8*(1)/(350)[130-25] (x^3)/(20.92*10^(-6)^2)](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/engineering/college/chk8i671ynbhjnz8825mibgxvgcbdigxh5.png)
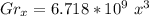
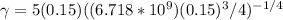
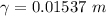
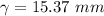
Hence, the boundary layer thickness at a location 0.15 m measured from the lower edge is 15.37 mm
b) The maximum velocity in the boundary layer
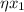 with f'(n) = 0.275
with f'(n) = 0.275
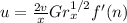
![u= (2*20.92*10^(-6))/(0.75) [6.718*10^9(0.15)^3]^(1/2) * 0.275](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/engineering/college/jic9ym6uwqcj5jr08wkw00r2sbm0vxkt0i.png)
u = 0.3659 m/s
the maximum velocity in the boundary layer at this location is 0.3659 m/s
the position in the boundary layer where the maximum occur is calculated as:
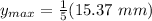
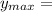 3.074 mm
3.074 mm
c) Using the similarity solution result, , determine the heat transfer coefficient 0.15 m from the lower edge.
we know that:
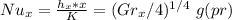
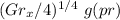 =
=
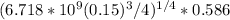
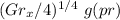 = 28.593
= 28.593
Making
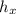 the subject from the above formula:
the subject from the above formula:
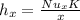
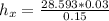
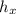 = 5.7186 W/m². K
= 5.7186 W/m². K
d) to determine the location on the plate that the boundary layer we become turbulent ; we have the following:
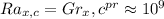
![x_c = [10^9/6.718*10^9(0.7)]^(1/3)](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/engineering/college/zij6ap3zejrrxldbaqdstv42g44hn84fdf.png)
 0.60 m
0.60 m