Answer:
a) - 122 kJ/kg
b) 0.117 kJ/kg K
Step-by-step explanation:
Given that:
at inlet condition:
Pressure
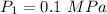
Temperature
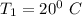
at Outlet condition:
Pressure
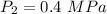
Temperature
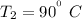
Heat transfer Q = 0
determine a) the power required by the compressor (kJ/kg)
Applying energy equation to the compressor work by the equation:
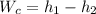
from propane of tables at the given conditions of temperature and pressure; we obtain the following enthalpies

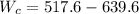
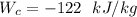
Thus, the power required by the compressor is - 122 kJ/kg
b) the change in specific entropy of propane (kJ/kg K) at the outlet and the inlet of the compressor.
Taking entropies from the propane tables at given conditions of pressure and temperature
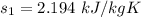
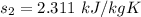
Thus; the rate of entropy production is :
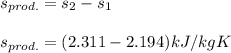
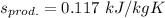
Thus; the change in specific entropy of propane (kJ/kg K) at the outlet and the inlet of the compressor is 0.117 kJ/kg K