Answer:
Step-by-step explanation:
To start with the mass at the entrance of the channel
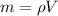
where
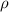 = density of water = 62.37 lb/ft³
= density of water = 62.37 lb/ft³
V = velocity of the flow = 100 ft³/s
m = 62.37 lb/ft³ × 100 ft³/s
m = 6237 lb/s
m = 62.37 × 10² lb/s
Since the channels are identical, the mass flow rate are as well equal in both sections i.e
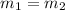
Also; the flow rate is noted to be at a steady state, frictionless and the fluid is deemed to be incompressible
Therefore using the law of conservation of mass flow:
m =
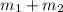
m =
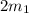
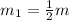
Applying the momentum equilibrium for steady one-dimensional flow:
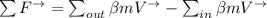
Considering the momentum equation along the x-axis is:
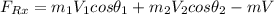
where;
m = mass flow rate before hitting the splliter
V = velocity of flow before hitting the splliter
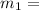 mass flow rate channel one
mass flow rate channel one
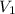 = velocity flow rate channel one
= velocity flow rate channel one
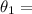 angle by the spit channel one to the horizontal
angle by the spit channel one to the horizontal
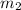 = mass flow rate channel two
= mass flow rate channel two
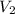 = velocity flow rate channel two
= velocity flow rate channel two
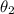 = angle by the spit channel two to the horizontal
= angle by the spit channel two to the horizontal
From the above recent equation:
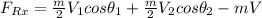
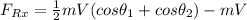
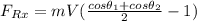
Replacing our values :
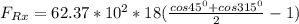
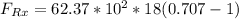
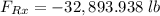
Thus, the force needed in the x-direction to keep the splliter position is 32,893.938 lb (i.e in the opposite direction of the water jet)
Again:
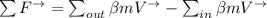
Considering the momentum equation along the z-axis is:
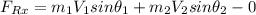
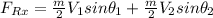
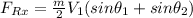
Replacing our values :
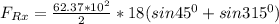
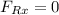
Thus, there is no force needed in the z-direction. Since the forces are equal and opposite in direction to each other.