Answer:
The volume of the gas at a pressure of 65.0 kPa would be 363 mL
Step-by-step explanation:
Boyle's Law is a gas law that relates the pressure and volume of a certain amount of gas, without temperature variation, that is, at constant temperature.
Boyle's law states that the pressure of a gas in a closed container is inversely proportional to the volume of the container, when the temperature is constant. In other words, the product P · V remains constant at the same temperature:
P*V=k
Being P1 and V1 the pressure and volume in state 1 and P2 and V2 the pressure and volume in state 2 are fulfilled:
P1*V1=P2*V2
In this case:
- P1= 45 kPa= 45,000 Pa (being 1 kPa=1,000 Pa)
- V1= 525 mL= 0.525 L (being 1 L=1,000 mL)
- P2= 65 kPa= 65,000 Pa
- V2= ?
Replacing:
45,000 Pa* 0.525 L= 65,000 Pa*V2
Solving:
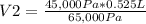
V2=0.363 L=363 mL
The volume of the gas at a pressure of 65.0 kPa would be 363 mL