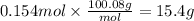Answer:
15.4 g
Step-by-step explanation:
Let's consider the decomposition of calcium carbonate to form carbon dioxide.
CaCO₃ → CaO + CO₂
Step 1: Calculate the moles of carbon dioxide
Since the conditions are not explicit, we will suppose that CO₂ is at standard temperature and pressure (STP). In these conditions, 1 mole of any gas has a volume of 22.4 L (assuming ideal behavior).
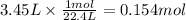
Step 2: Calculate the moles of calcium carbonate
The molar ratio of CaCO₃ to CO₂ is 1:1. Then, the moles of CaCO₃ required are 0.154 moles.
Step 3: Calculate the mass of calcium carbonate
The molar mass of CaCO₃ is 100.09 g/mol. Then,