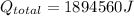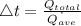Answer:
Average convection heat transfer coefficient,
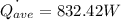
time taken for the process,
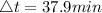
Step-by-step explanation:
The average convection heat transfer rate is calculated using the formula:
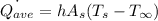
The surface area of the steel ball is given by :
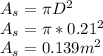
Free stream temperature,
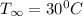
Initial temperature of the ball, T₁ = 350°C
Final temperature of the ball, T₂ = 250°C
Average surface temperature of the ball:
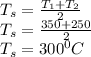
Velocity of air, V = 6 m/s
Diameter of the ball, D = 0.21 m
Viscosity, v = 1.608 * 10⁻⁵ m²/s
Reynold number Re can be calculated by using the formula:
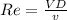
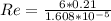
Re = 78358.21
The Nusselt number can be calculated by using the equation:
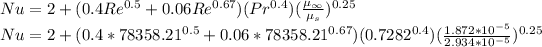
Nu = 179.95
The heat transfer coefficient can be calculated using the formula:
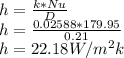
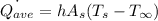
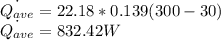
The time taken for the process,
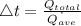
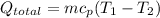
Volume of the steel ball,
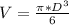
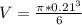
V = 0.0049 m³
Density of steel,
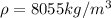
Mass of the steel,
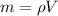
m = 8055*0.0049
m = 39.47 kg
Total rate of heat transfer:
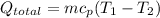
Specific heat capacity of steel ball,
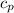 = 480 J/kg
= 480 J/kg