Answer:
We conclude that the population mean number of eggs laid per chicken is different from 21 eggs.
Explanation:
We are given that the owner of Youtbia Farm wants to estimate the mean number of eggs laid per chicken.
A sample of 20 chickens shows they laid an average of 20 eggs per month with a standard deviation of 2 eggs per month.
Let
 = population mean number of eggs laid per chicken.
= population mean number of eggs laid per chicken.
So, Null Hypothesis,
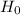 :
:
 = 21 eggs {means that the population mean number of eggs laid per chicken is 21 eggs}
= 21 eggs {means that the population mean number of eggs laid per chicken is 21 eggs}
Alternate Hypothesis,
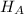 :
:

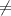 21 eggs {means that the population mean number of eggs laid per chicken is different from 21 eggs}
21 eggs {means that the population mean number of eggs laid per chicken is different from 21 eggs}
The test statistics that would be used here One-sample t test statistics as we don't know about the population standard deviation;
T.S. =
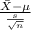 ~
~
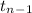
where,
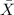 = sample average number of eggs laid per chicken = 20 eggs
= sample average number of eggs laid per chicken = 20 eggs
s = sample standard deviation = 2 eggs
n = sample of chickens = 20
So, the test statistics =
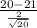 ~
~
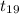
= -2.236
The value of t test statistics is -2.236.
Since, in the question we are not given with the level of significance so we assume it to be 5%. Now, at 5% significance level the t table gives critical values of - 2.093 and 2.093 at 19 degree of freedom for two-tailed test.
Since our test statistic doesn't lie within the range of critical values of t, so we have sufficient evidence to reject our null hypothesis as it will fall in the rejection region due to which we reject our null hypothesis.
Therefore, we conclude that the population mean number of eggs laid per chicken is different from 21 eggs.