Answer:
All of the above
Step-by-step explanation:
The magnitude of the magnetic force on a current-carrying wire held in a magnetic is given by the equation
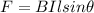
Where B = Strength of the magnetic field
I = The current carried by the wire
l = length of the wire in the magnetic field
θ = Angle between the wire and the magnetic field
Based on the relationship written above, the magnitude of the magnetic force on the current - carrying wire in the magnetic field depends on the strength of the magnetic field (B), length of the wire(l), current in the wire (I).
All the options are correct.