Answer:
The deceleration of the dragster upon releasing the parachute such that the wheels at B are on the verge of leaving the ground is 16.33 m/s²
Step-by-step explanation:
The additional information to the question is embedded in the diagram attached below:
The height between the dragster and ground is considered to be 0.35 m since is not given ; thus in addition win 0.75 m between the dragster and the parachute; we have: (0.75 + 0.35) m = 1.1 m
Balancing the equilibrium about point A;
F(1.1) - mg (1.25) =
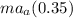
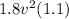 - 1200(9.8)(1.25) = 1200a(0.35)
- 1200(9.8)(1.25) = 1200a(0.35)
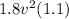 - 14700 = 420 a ------- equation (1)
- 14700 = 420 a ------- equation (1)
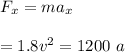 --------- equation (2)
--------- equation (2)
Replacing equation 2 into equation 1 ; we have :
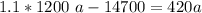
1320 a - 14700 = 420 a
1320 a - 420 a =14700
900 a = 14700
a = 14700/900
a = 16.33 m/s²
The deceleration of the dragster upon releasing the parachute such that the wheels at B are on the verge of leaving the ground is 16.33 m/s²