Answer:
Check the explanation
Step-by-step explanation:
cell CuE Ecell 0.337 (-0.14) Ecl0.477 V
Since
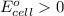 , the value of \Delta G^o will be negative.
, the value of \Delta G^o will be negative.
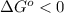
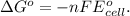 .....(1)
.....(1)
But
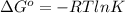 ......(2)
......(2)
From (1) and (2)
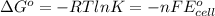
ln K =
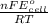
ln K =
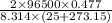
ln K =37.139
K =
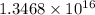
Hence, the value of the equilibrium constant is
