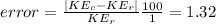Answer:
1.32% error
Step-by-step explanation:
You can derive the relativistic kinetic energy by integrating the velocity function over a differential change in momentum. Then use integration by parts to get the answer of:
![KE=mc^2[gamma-1]](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/physics/college/5wr9duhy0wn1zmi2nfr9nrxo7v1u2xodjd.png)
Gamma is the lorentz factor equal to:
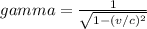
Therefore the relativistic kinetic energy would be:
![KE=mc^2[(1)/(√(1-(v/c)^2))-1]](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/physics/college/jnqf911cnssso6vxe70sggzfdr56ps4kiz.png)
Plug everything in to get:
![KE=(17000)(3x10^8)^2[(1)/(√(1-(0.14c/c)^2))-1]](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/physics/college/ht3x5ug86ux5bje3vhejfjgj1uok3xqv1j.png)
![KE=(17000)(9x10^(16))[(1)/(√(1-0.0196))-1]](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/physics/college/4vxls92wsab0qendmflx1xk75akbiiijjk.png)
![KE=1.53x10^(21)[(1)/(√(1-0.0196))-1]](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/physics/college/b2fp1vwpmom1el5wulh9qz9vmlhzzmodq0.png)
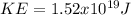
The classical non-relativistic formula for kinetic energy is:
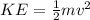
Therefore the classical kinetic energy is:
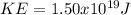
Use the error percentage formula, found online if you dont recall: