Answer:
a) We want to test to determine if there has been a significant increase in the average yearly income of dentists, the system of hypothesis would be:
Null hypothesis:
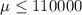
Alternative hypothesis:
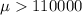
b)
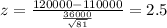
c)
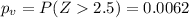
We see that the p value is lower than the significance level of
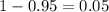 so then we can conclude that the true mean is significantly higher than 110000 because we reject the null hypothesis.
so then we can conclude that the true mean is significantly higher than 110000 because we reject the null hypothesis.
Step-by-step explanation:
Information given
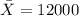 represent the sample mean for the yearly income in 2006 for the dentists
represent the sample mean for the yearly income in 2006 for the dentists
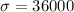 represent the sample population deviation
represent the sample population deviation
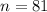 sample size
sample size
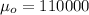 represent the value that we want to test
represent the value that we want to test
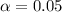 represent the significance level
represent the significance level
z would represent the statistic
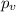 represent the p value for the test
represent the p value for the test
a) Hypothesis to verify
We want to test to determine if there has been a significant increase in the average yearly income of dentists, the system of hypothesis would be:
Null hypothesis:
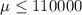
Alternative hypothesis:
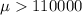
Since we know the population deviation the statistic is given by:
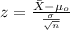 (1)
(1)
b) Statistic
When we replace the data given we got:
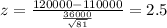
c) P value
Now we can find the p value using the fact that we are conducting a right tailed test:
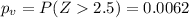
We see that the p value is lower than the significance level of
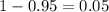 so then we can conclude that the true mean is significantly higher than 110000 because we reject the null hypothesis.
so then we can conclude that the true mean is significantly higher than 110000 because we reject the null hypothesis.