Answer:
Step-by-step explanation:
a) Please see the attached image below.
b) The magnitude of the magnetic field generated by the current in a wire is given by:
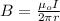
μo: magnetic permeability of vacuum = 4π*10^-7 T/A
I: current = 850A
r: distance where B is calculated = 2.00cm = 0.02m
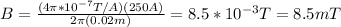
As you can see in the image, the direction of B points inside the sheet of paper.
c) The magnetic force is given by:
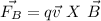
You can assume that the direction of B is in -z direction, that is, -k. Thus, the direction of the proton is in +x direction, or +i. The direction of the magnetic force over the proton is given by the following cross product:
i X (-k) = - (i X k) = -(-j) = j
Then, the direction of FB is in +y direction, that is, upward respect to the wire.
The magnitude of FB will be:
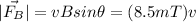
(it is only necessary to replace by the value of v)