Answer:
A) 0.981 atm
B) 7.89 × 10⁻⁴ moles
C) 25.348 grams ≈ 25.3 grams
D) 4.315% increase error in molar mass
Step-by-step explanation:
A) The partial pressure of the water vapor = 0.029 atm.
Total gas pressure in the tube = 1.01 atm
Therefore, by Dalton's law of partial pressure, the total pressure of a given mass of gas is equal to the sum of the partial pressures of the individual gases in the mixture
Hence, total pressure = partial pressure of H₂ + Partial pressure of water vapor
1.01 atm = partial pressure of H₂ + 0.029 atm.
∴ Partial pressure of H₂ = 1.01 atm - 0.029 atm = 0.981 atm
The partial pressure of the dry hydrogen gas collected in the tube = 0.981 atm
B) From the universal gas equation, we have;
PV = nRT
Therefore,
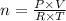
Where:
n = Number of moles
P = Pressure = 0.981 atm
V = Volume = 19.6 ml
T = Temperature = 24° = (273.15 + 24) K = 297.15 K
R = Universal Gas Constant = 0.08205 L·atm/(mol·K)
Plugging in the values, we have;
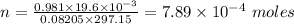
The number of moles of hydrogen gas collected = 7.89 × 10⁻⁴ moles
C) Since 1 mole of M reacts with 1 mole of H₂SO₄ in the reaction, we have
0.500 M of H₂SO₄ will react with 0.500 M of M
From;
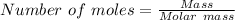 we have;
we have;
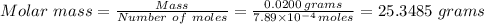
D) The
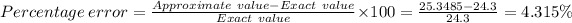 is
is
Given that the actual molar mass = 24.3 g/mol.
The percentage error in the experimental molar ≈ 4.315%.