To determine the [OH⁻], pH, and pOH of a solution with a given [H⁺], you can use the following relationships:
- OH⁻ and pOH Relationship:
pOH = -log[OH⁻]
- [H⁺] and pH Relationship:
pH = -log[H⁺]
pH} + pOH = 14
Given [H⁺] =
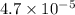 M, we can calculate the corresponding values:
M, we can calculate the corresponding values:
![\[ \text{pOH} = -\log(4.7 * 10^(-5)) \]](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/dijupmuk7m9nis9dwl9livxp708a03d1un.png)
![\[ \text{pOH} \approx 4.33 \]](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/vn28qkaod9l197vw2vnura4ahx43uwj6v5.png)
![\[ \text{pOH} + \text{pH} = 14 \]](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/avxun1pxwyyqgmrjp80jq4cd4pqeiy24ji.png)
![\[ \text{pH} = 14 - \text{pOH} \]](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/fiy0ieqme263r1m3o2zhrm72zpe8854w05.png)
![\[ \text{pH} \approx 14 - 4.33 \]](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/rxuh6izu3tsclicso1fu1k4s5ei9fwjnp8.png)
![\[ \text{pH} \approx 9.67 \]](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/m7vptyoow0wln8m2xawc8k90f00efe92nk.png)
[OH⁻]:
![\[ \text{pOH} = -\log[\{OH^-}] \]](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/cqjxxsh25h41joqgvx1wmrslh084w8gxoo.png)
4.33 = -log[OH⁻]
[OH⁻] =
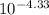
![\[ [\{OH^-}] \approx 2.04 * 10^(-5) \, \text{M} \]](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/cgbui8nw5zx0sc0t7xmzpnw650u7367ppk.png)
So, for the given solution: