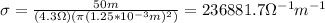Answer:
a) 1273.23 A/m^2
b) 7.19*10^-5 m/s
c) 236881.7 Ohms
Step-by-step explanation:
(a) To find the current density you use the following formula:
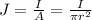
I: current in the wire
A: cross area of the wire
r: radius of the wire
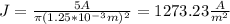
(b) The electron drift speed is given by:
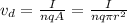
n: number of conduction electrons per m^3
q: charge of the electron = 1.6*10^-19C
The number of free electrons is calculated by using:
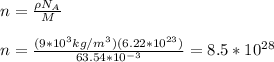
Next, you replace the values of the parameters in the equation for vd:
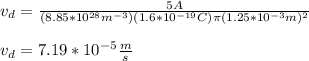
(c) The conductivity is given by:
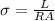
You first calculate R:
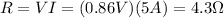
Next, replace for sigma: