Answer:
Explanation:
Given that :
St = the event that person is statistician
E = the event that person is Economist
Sh = the event that person is Shy
a. Briefly explain what key assumption is necessary to validly bring probability into the solution of this problem?
St and E are exclusive events since a person cannot be both statistician and economist.
Key Assumptions:
P(St) + P(E) = 1
Also;
P (St ∩ E) = ∅
b. Using the St. E and Sh notation, express the three numbers (80%, 15%, 90%) above and the probability we're solving for, in unconditional and conditional probability terms.
Given that :
80 % (0.8) of the statisticians are shy and also 15% (0.15) of the economist too are shy; Then :
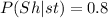
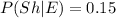
In the conference; it is stated that there are 90% economist ; Therefore:
P(E) = 0.9
P(St) = 0.1
c) Briefly explain why calculating the desired probability is a good job for Bayes's The- orem
From the foregoing; we knew the probability of
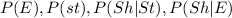 and asked to show that P(st|sh) = 0.37 ; Then using Bayes Theorem; we have:
and asked to show that P(st|sh) = 0.37 ; Then using Bayes Theorem; we have:
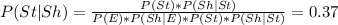
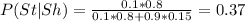
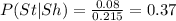
As illustrated above; the required probability was determined using Bayes Theorem; Thus, calculating the desires probability is a good job for Bayes's The- orem.