Answer:
For air
The pressure downstream of normal shock is 447.76 kPa
The temperature downstream of normal shock is 604.26 K
The mach number downstream of normal shock is 0.504
The velocity of air downstream of normal shock is 248.2 m/s
The stagnation pressure downstream of normal shock is 532.498 kPa
For helium
The pressure downstream of normal shock is 475.89 kPa
The temperature downstream of normal shock is 801.36 K
The mach number downstream of normal shock is 0.546
The velocity of air downstream of normal shock is 309.64 m/s
The stagnation pressure downstream of normal shock is 603.258 kPa
the values of the temperature,
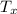 , pressure,
, pressure,
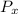 , velocity, v and mach number,
, velocity, v and mach number,
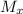 are higher downstream for helium than for air
are higher downstream for helium than for air
Change in entropy, Δ
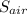 for air is 7.333 J/K
for air is 7.333 J/K
Change in entropy,
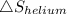 for helium is 5.784 J/K
for helium is 5.784 J/K
Step-by-step explanation:
Here we have the relations and ratios from compressible flow tables for normal shock as follows;
For Mach number, 2.6 the values of the relations are;
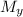 = 0.504
= 0.504
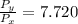
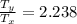
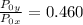
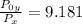
Where:
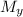 = Mach number downstream of normal shock
= Mach number downstream of normal shock
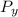 = Pressure downstream of normal shock
= Pressure downstream of normal shock
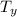 = Temperature downstream of normal shock
= Temperature downstream of normal shock
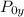 = Stagnation pressure downstream of normal shock
= Stagnation pressure downstream of normal shock
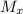 = Mach number upstream of normal shock = 2.6
= Mach number upstream of normal shock = 2.6
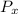 = Pressure upstream of normal shock = 58 kPa
= Pressure upstream of normal shock = 58 kPa
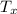 = Temperature upstream of normal shock = 270 K
= Temperature upstream of normal shock = 270 K
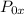 = Stagnation pressure upstream of normal shock
= Stagnation pressure upstream of normal shock
Therefore;
From;
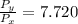
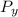 =
=
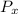 × 7.720 = 58 kPa × 7.720 = 447.76 kPa
× 7.720 = 58 kPa × 7.720 = 447.76 kPa
From;
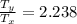
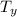 =
=
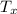 × 2.238 = 270 K × 2.238 = 604.26 K
× 2.238 = 270 K × 2.238 = 604.26 K
From;
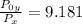
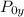 =
=
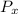 × 9.181 = 58 kPa × 9.181 = 532.498 kPa
× 9.181 = 58 kPa × 9.181 = 532.498 kPa
Velocity of sound in air at 604.26 K is given by the following relation;
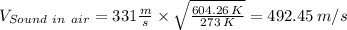
The velocity of the air is then found from the relation;
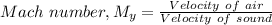
Therefore;
Velocity of air downstream of normal shock = 492.45 m/s × 0.504 = 248.2 m/s
For helium, γ = 1.667 from where we obtain from similar tables the relationship as follows;
Here we have the relations and ratios from compressible flow tables for normal shock as follows;
For Mach number 2.6 the values of the relations are;
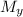 = 0.546
= 0.546
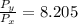
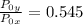
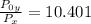
Solving as before, where:
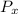 = Pressure upstream of normal shock = 58 kPa
= Pressure upstream of normal shock = 58 kPa
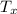 = Temperature upstream of normal shock = 270 K
= Temperature upstream of normal shock = 270 K
We have;
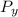 =
=
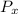 × 8.205 = 58 kPa × 8.205 = 475.89 kPa
× 8.205 = 58 kPa × 8.205 = 475.89 kPa
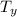 =
=
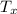 × 2.968 = 270 K × 2.968 = 801.36 K
× 2.968 = 270 K × 2.968 = 801.36 K
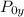 =
=
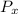 × 10.401 = 58 kPa × 10.401 = 603.258 kPa
× 10.401 = 58 kPa × 10.401 = 603.258 kPa
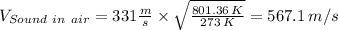
Velocity of helium downstream of shock =
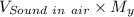
= 567.1 m/s × 0.546 = 309.64 m/s
Therefore, the values of the temperature,
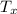 , pressure,
, pressure,
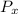 , velocity, v and mach number,
, velocity, v and mach number,
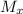 are higher downstream for helium than for air.
are higher downstream for helium than for air.
The entropy change is given by the following relation;
Change in entropy = ΔS
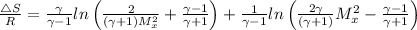
Where:
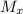 is given as 2.6
is given as 2.6
For air, γ = 1.4
For helium γ = 1.67
R = Universal gas constant
Plugging in the values, we have;
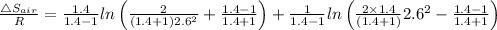
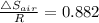
∴ Δ
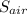 = R × 0.882 = 8.3145 × 0.882 = 7.333 J/K
= R × 0.882 = 8.3145 × 0.882 = 7.333 J/K
Similarly
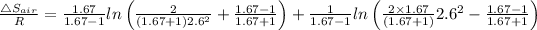
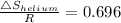
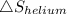 = R × 0.696 = 8.3145 × 0.696 = 5.784 J/K.
= R × 0.696 = 8.3145 × 0.696 = 5.784 J/K.