Answer:
A.
$0.05
B.
$18,600
C.
30,000 units
Step-by-step explanation:
Economic order quantity is the quantity at which business incur minimum cost. This is the level of order where the holding cost equals to the ordering cost of the business.
As per given data
Annual Demand = 90,000 batteries
Ordering cost = $250
Carrying cost = $0.046
A.
Annual Holding cost = Holding cost per unit x Annual Demand = $0.046 x 90,000 batteries = $4,140
Opportunity cost = $0.046 X 110% = $0.05
B.
Purchase cost = 90,000 x $0.14 = $12,600
Ordering cost = (90,000/15,000) x $250 = $1,500
Storage cost = $0.05 x 90,000 = $4,500
Total cost of Inventory = $12,600 + $1,500 + $4,500 = $18,600
C.
EOQ =
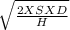
EOQ =
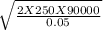
EOQ = 30,000