Answer:
Step-by-step explanation:
Given: i. in the AC series circuit, V = √2
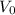 cos(ωt)], L and R.
cos(ωt)], L and R.
ii. in the DC circuit, R, L and
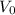 .
.
1. To show that average power through resistor in the AC circuit is the same in the DC circuit, when L = 0.
For the AC circuit,
Average power =
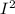 Z
Z
where: I is the current flowing and Z is the impedance.
Impedance, Z =
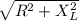
But,
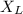 = 2
= 2
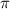 fL
fL
⇒
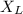 = 0 (∵ L = 0)
= 0 (∵ L = 0)
So that, Impedance, Z = R
Thus, average power through the resistor in the AC circuit =
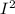 R
R
For the DC circuit,
Average power =
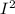 R
R
Therefore,
the average power through the resistor in the AC circuit = the average power through the resistor in the DC circuit =
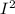 R, when L = 0.
R, when L = 0.
2. In the AC circuit, the expression for the peak current,
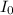 can be determined by:
can be determined by:
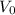 =
=
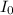 × Z
× Z
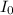 =
=
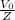
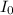 =
=
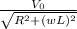
3. The frequency that would produce average power in the AC circuit is;
Average power =
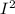 Z
Z
Average power =
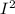 (
(
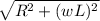
Square both sides to have;
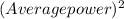 =
=
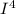 (
(
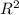 +
+
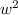
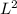 )
)
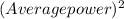 -
-
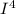
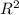 =
=
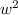
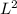
⇒
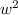 = [
= [
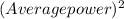 -
-
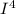
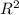 ] ÷
] ÷
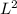
ω =
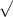 {[
{[
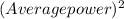 -
-
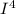
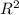 ] ÷
] ÷
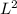 }
}
Therefore, frequency, ω =
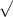 {[
{[
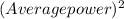 -
-
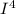
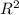 ] ÷
] ÷
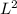 } is required to produce average power in the resistor in the AC circuit compared to the DC circuit.
} is required to produce average power in the resistor in the AC circuit compared to the DC circuit.