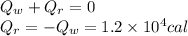Answer:
1.2 × 10⁴ cal
Step-by-step explanation:
Given data
- Initial temperature: 80 °C
We can calculate the heat released by the water (
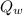 ) when it cools using the following expression.
) when it cools using the following expression.
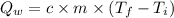
where
c is the specific heat capacity of water (1 cal/g.°C)
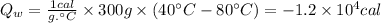
According to the law of conservation of energy, the sum of the heat released by the water (
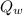 ) and the heat absorbed by the reaction (
) and the heat absorbed by the reaction (
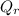 ) is zero.
) is zero.