Answer:
The equilibrium constant K is 0.1967
Step-by-step explanation:
Chemical equilibrium is a state of a reacting system in which no observed changes over time, even though the reaction continues. It occurs in reversible reactions, where the rate of reaction of reagents to products is the same as that of products to reagents.
The chemical equation can be written as:
a A + b B → c C + d D
Where a, b, c, d are the stoichiometric coefficients of the reaction and A, B, C, D are the symbols or formulas of the different substances involved.
The equilibrium constant K can be defined as the ratio between the product between the concentrations of the products (in equilibrium) raised to their corresponding stoichiometric coefficients, and the product of the concentrations of the reactants (in equilibrium) raised in their corresponding stoichiometric coefficients:
![Kc=([C]^(c) *[D]^(d) )/([A]^(a) *[B]^(b) )](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/high-school/sq0y109vxrlor0lre5d7gtd4e1lmwzjnp6.png)
In this case:
![Kc=([CO]*[H_(2)O] )/([CO_(2)]*[H_(2)] )](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/middle-school/prbumz358xlpy8g0h6hawqwefa4y08xfu9.png)
You know that:
Replacing:
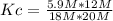
Kc= 0.1967
The equilibrium constant K is 0.1967