Answer:
(a). With fewer molecules in the container, the molecules have lower average speeds.
(b). With fewer molecules per unit volume, the molecules hit the walls of the container less often.
(c). With lower average speeds, on average the molecules hit the walls of the container with less force.
Step-by-step explanation:
Ideal gas law is given as;
PV = nRT
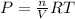
Where;
P is the pressure of the gas
V is the volume of the gas
n is the number of moles of the gas (amount of gas )
R is ideal gas constant
T is the temperature of the gas
If the amount of gas is decreased, while the volume and temperature are held constant, the pressure will decrease because number of gas moles per unit volume
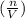 will be reduced, causing the entropy of the gas to be reduced since entropy decreases with decrease in gas molecules.
will be reduced, causing the entropy of the gas to be reduced since entropy decreases with decrease in gas molecules.
As the entropy of the gas molecules reduce, the average speed of the gas molecules will be reduced as well, this will cause fewer collision of the gas molecules with the walls of the container ( i.e on average the gas molecules hit the walls of the container with less force since force is directly proportional to speed, and less force implies less pressure since the contact surface is constant).
Choosing all that apply:
- (a). With fewer molecules in the container, the molecules have lower average speeds.
- (b). With fewer molecules per unit volume, the molecules hit the walls of the container less often.
- (c) . With lower average speeds, on average the molecules hit the walls of the container with less force.