Answer:
About 64 grams of KClO₃.
Step-by-step explanation:
Potassium chlorate dissociates according to the equation:
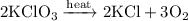
To determine the amount of KClO₃ necessary to produce 25 grams of O₂, we can convert grams of O₂ to moles; moles of O₂ to moles of KClO₃; and finally to grams of KClO₃.
The molecular weights of O₂ and KClO₃ are 16.00 g/mol and 122.55 g/mol.
Hence:
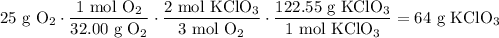
In conclusion, about 64 (to two significant digits) grams of KClO₃ is needed.