Answer:
The correct answer to the following question will be "v = 3.30×10⁵ m/s".
Step-by-step explanation:
Electron collisions may initially have led to a change or transition from, n = 1 to n = 3.
So,
Incident electrons lost (-6.5-(-2)) = -4.5 ev at energy.
From energy management,
⇒
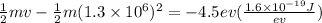
On taking "m" common, we get
⇒
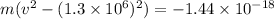
⇒
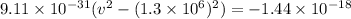
⇒
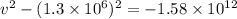
⇒
