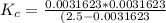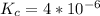Answer:
The correct option is C
Step-by-step explanation:
From the question we are told that
The concentration of the acid solution is
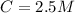
The pH of the acid is
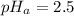
Looking at the pH of the acid we can say that it is a strong acid
This because its pH fall between 0-7
The generally dissociation chemical equation for this acid is represented as
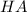 ⇄
⇄
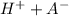
So the equilibrium constant for this reaction is mathematically represented as
![K_c = ([H^+] [A^-])/([HA])](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/iccegt0uc7r11hctucac8v4ka2vfcyeals.png)
and the pH of can be mathematically represented as
![pH = -log [H^+]](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/xa144nmf94yab1614tqi33k1rma1zeqe9n.png)
=>
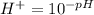
substituting value
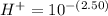
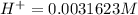
Looking at the chemical equation we see that the ratio of the moles for the product is one is to one
Secondly the new concentration of the reactant will be

![[A^-] = 0.003163 M](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/hznzdjk6k6wcjzle0hpfx6sbcyi8amcgyw.png)
So the equilibrium constant is