Answer:
8cm
Step-by-step explanation:
Here, two disc are identical and rolling on the horizontal surface
Also,while disc is in rolling motion its kinetic energy is sum of rotational kinetic energy and transnational kinetic energy.
Therefore,
KE =
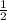 mv²+
mv²+
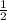
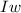 ²
²
For pure rolling of disc we have:
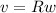
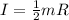 ²
²
By substituting in KE eq, we get
KE =
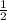 mv²+
mv²+
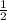 (
(
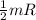 ²)(
²)(
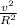 )
)
KE=
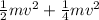
The total kinetic energy will convert into gravitational potential energy when disc roll over the inclined surface.
mgH=
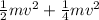 =>
=>
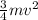
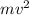 = 4/3mgH
= 4/3mgH
If another disc rolls up on frictionless inclined plane then it will lose all its translational kinetic energy but rotational kinetic energy will remain as it is as there is no torque on the disc
Therefore, mgh= 1/2mv²
1/2mv²= 4/3mgH
mgh=2/3mgH
h=2/3H
Height = 12cm is given
h= 8cm
Thus, Disk B reaches a height of 8cm above the floor.