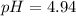Complete Question
The complete question is shown on the first uploaded image
Answer:
The pH is
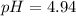
Step-by-step explanation:
From the question we are told that
The average concentration of NaOH is
![[NaOH] = 0.101 M](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/j1fbhuh0x4qjberxlt1232etamw9s8j2lp.png)
The volume of NaOH is
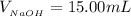
The average concentration of Acetic acid is
![[Acetic \ Acid] =0.497 \ M](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/gr8fj11l490uxk4r040ntynhgb6og7b1jk.png)
The volume of Acetic acid is
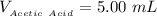
The chemical equation for this reaction is

The total volume of the solution is
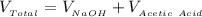
Substituting values
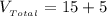
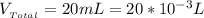
The number of moles of NaOH is mathematically represented as
![n__(NaOH)} = [NaOH] * V__(NaOH)}](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/fes33ll7fm2e8881p1y80h9mhcrqnbya7j.png)
substituting values
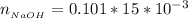
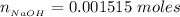
The number of moles of Acetic acid is mathematically represented as
![n__(Acetic acid)} = [Acetic \ acid] * V__(Acetic acid)}](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/kctz0aoejs5fa95jufvbxx8z8hlnheacx5.png)
substituting values
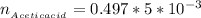
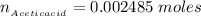
From the chemical equation
1 mole of NaOH reacts with 1 mole of Acetic acid to produce 1 mole of
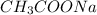 salt and 1 mole of
salt and 1 mole of
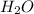
So
0.001515 moles of NaOH reacts with 0.001515 moles of Acetic acid to produce 0.001515 moles of
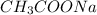 salt and 0.001515 moles of
salt and 0.001515 moles of
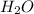
This implies the number of moles of NaOH remaining after the react would be
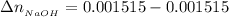
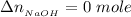
the number of moles of Acetic acid remaining after the react would be
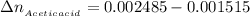
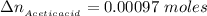
the number of moles of
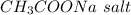 remaining after the react would be
remaining after the react would be
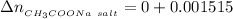
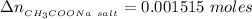
the number of moles of
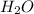 remaining after the react would be
remaining after the react would be
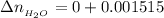
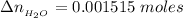
The expected pH is mathematically evaluated as
![pH = pK_a + log [([CH_3 COONa])/([Acetic \ acid]) ]](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/5ablcxllj0cegov2dbam1id53owpboz957.png)
Where
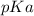 is mathematically evaluated as
is mathematically evaluated as
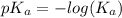
The concentration of
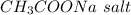 is mathematically evaluated a s
is mathematically evaluated a s
![[CH_3 COONa] = (\Delta n_CH_3 COONa \ salt )/(V__(Total))}](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/bnv4wc9fqwb8qa5dmhtgwnk6q6lnhp3bvo.png)
substituting values
![[CH_3 COONa] = (0.001515)/(20 *10^(-3))](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/9gv52gibvkjnszn7sycdr9vs056f6kvg3j.png)
![[CH_3 COONa] = 0.07575M](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/maoh85m5dqyues8lk9q8bgr5k235srr19o.png)
The concentration of Acetic acid is mathematically evaluated as
![[Acetic acid] = (\Delta n__Acetic acid)/(V__(Total))}](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/3ivyl066q7xp2ekladd9c9aim9p69r5rfm.png)
substituting values
![[CH_3 COONa] = (0.00097)/(20 *10^(-3))](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/msp7jq3rr8noogdzij6pmz0m75uz1mzvn4.png)
![[CH_3 COONa] = 0.0485 M](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/vr2fgt4jvyji8f7ablrp6kg4e41zcc0m1p.png)
Substituting values into the equation for pH
![pH = - log (1 .8 *10^(-5)) + log [(0.07575)/( 0.0485) ]](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/ya96orz4727zzozrp38vbc7sh886tkvijk.png)
![pH = log [(0.07575)/( 0.0485) ] - log (1 .8 *10^(-5))](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/d2tur6u1v3kd6rbl1t51w38ckdrj0drlk0.png)
![pH = log [(1.561856)/(1.8*10^(-5)) ]](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/fneh9131nduz92u7s7r772k6lhw0ew76yy.png)