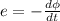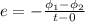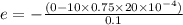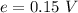Answer:0.15 V
Step-by-step explanation:
Given
Dimension of coil

Area of coil
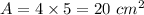
Magnetic field
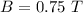
Time of rotation
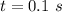
No of turns
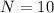
Initial flux associated with the coil
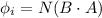
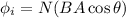
where
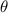 =angle between magnetic field and area vector of coil
=angle between magnetic field and area vector of coil
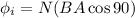
Finally when coil is perpendicular to the field
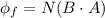
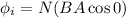
and induced emf is given by