Answer:
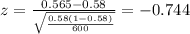
Since is a bilateral test the p value would be given by:
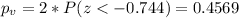
And since the p value is higher than the significance level we have enough evidence to conclude that the true proportion is not significantly different from 0.58
Explanation:
Information given
n=600 represent the random sample selcted
X=339 represent the number of females aged 15 and older that living alone
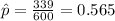 estimated proportion of females aged 15 and older that living alone
estimated proportion of females aged 15 and older that living alone
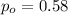 is the value that we want to check
is the value that we want to check
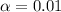 represent the significance level
represent the significance level
z would represent the statistic
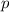 represent the p value
represent the p value
Sytem of hypothesis
We want to check if the true proportion females aged 15 and older that living alone is significantly different from 0.58.:
Null hypothesis:
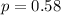
Alternative hypothesis:
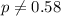
The statistic is given by:
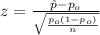 (1)
(1)
Replacing the info given we got:
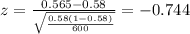
Since is a bilateral test the p value would be given by:
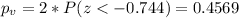
And since the p value is higher than the significance level we have enough evidence to conclude that the true proportion is not significantly different from 0.58