Answer:
Step-by-step explanation:
12.0 kv primary voltage
315 kv secondary voltage ( converted voltage ) V1 or Vo
v2 (Vn)= 730 kv new secondary voltage
a) Ratio of turns in 730 kv to turns in 315 kv
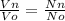 =
=
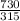 therefore the ratio of turns = 2.317 ≈ 2.32
therefore the ratio of turns = 2.317 ≈ 2.32
B) ratio of the new current output to the old current output for the same power input to the transformer
since the power input is the same
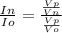 equation 1
equation 1
Vp = primary voltage, Vo = old secondary voltage, Vn = new secondary voltage, In = new secondary current, Io = old secondary current
therefore equation 1 becomes
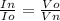 = 315 / 730 = 0.43
= 315 / 730 = 0.43