Answer:
The additional information required to solve this problem is the initial volume.
the final pressure P₂ of the gas is 1.108 atm
Step-by-step explanation:
Given that :
A sample of gas at initial temperature
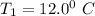 = (12+273)K = 285 K
= (12+273)K = 285 K
Pressure (P₁) = 1.06 atm
Initial Volume (V₁) = unknown ???
Final Volume (V₂) = 2.30 L
final temperature
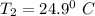 = (24.9 +273)K = 297.9 K
= (24.9 +273)K = 297.9 K
Find the final Pressure (P₂)
The relation between: Pressure, Volume and Temperature can be gotten from the ideal gas equation :
PV = nRT
The Ideal Gas Equation is also reduced to the General Gas Law or the combined Gas Law by assuming that n= 1 .
From ; PV = nRT
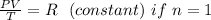
∴
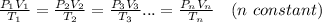
The additional information required to solve this problem is the initial volume.
This expression is a combination of Boyle's Law and Charles Law. From the combined Gas Law , it can be deduced that at constant volume, the pressure of a given mass(mole) of gas varies directly with absolute temperature.
∴
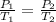 if n & Volume (V) are constant .
if n & Volume (V) are constant .
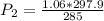
P₂ = 1.108 atm
Thus, the final pressure P₂ of the gas is 1.108 atm