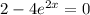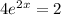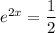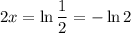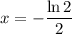1. Rewrite the expression in terms of logarithms:
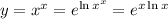
Then differentiate with the chain rule (I'll use prime notation to save space; that is, the derivative of y is denoted y' )
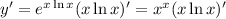
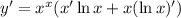
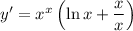
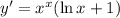
2. Chain rule:
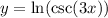
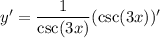
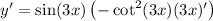
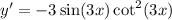
Since
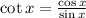 , we can cancel one factor of sine:
, we can cancel one factor of sine:
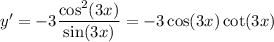
3. Chain rule:
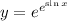
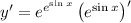
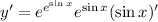
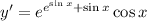
4. If you're like me and don't remember the rule for differentiating logarithms of bases not equal to e, you can use the change-of-base formula first:
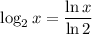
Then
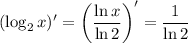
So we have
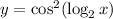
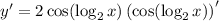
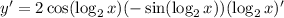
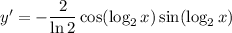
and we can use the double angle identity and logarithm properties to condense this result:
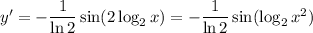
5. Differentiate both sides:
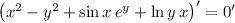
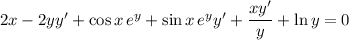
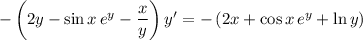
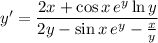
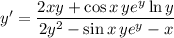
6. Same as with (5):
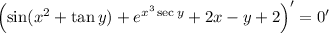
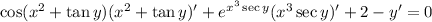
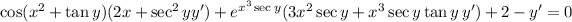
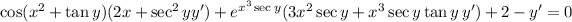
![\left(\cos(x^2+\tan y)\sec^2y+x^3\sec y\tan y\,e^(x^3\sec y)-1\right)y'=-\left(2x\cos(x^2+\tan y)+3x^2\sec y\,e^(x^3\sec y)+2\right)]()
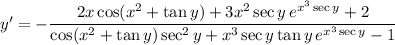
7. Looks like
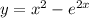
Compute the second derivative:
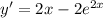
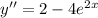
Set this equal to 0 and solve for x :